- You are here:
- Home /
- Products /
- Carbon Steel /
- Carbon Steel Sheet/Plate
High Strength Carbon Steel Plate for Structural and Industrial Use
Carbon steel plates in a wide range of grades and thicknesses. Suitable for bridges, machinery, pressure vessels, shipbuilding, and more. Available in cut-to-size, with fast delivery.
What Is Carbon Steel Plate?
Carbon steel plate is a flat steel sheet made from carbon-rich alloy with superior mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness. It is widely used in structural fabrication, machine parts, automotive frames, pressure vessels, and shipbuilding.
We supply carbon steel plates in:
- Mild Steel (Low Carbon)– Easy to cut, weld, and shape
- Medium/High Carbon– Better hardness and strength
- Boiler & Pressure Vessel Grade– Excellent toughness
- Shipbuilding Grade– High tensile, seawater-resistantAbrasion-Resistant Plate– For mining and construction
Products Link
- Alloy >>
- Heat-Resistant Steel
- Inconel Alloys
- Urea-Grade Steel
- Titanium Alloys
- Superalloys
- Super Duplex Stainless Steels
- Special Stainless Steels
- Soft Magnetic Alloys
- Precipitation Hardening Stainless
- Hydropower Steel
- Incoloy Alloys
- Super Austenitic Stainless Steels
- High-Strength Steels
- Monel Alloys
- Hastelloy Alloy
- Cobalt Based Alloy
- Stainless Steel >>
- Galvanized Steel >>
- Carbon Steel >>
- Aluminum Steel >>
Optional product specifications
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Steel Grades | Q195, Q235, Q345, 45#,1040,1060,A36, SS400, S235JR, S355JR, ASTM A516, A572, A588,NM400,NM450,NM600 |
| Thickness | 0.5mm – 300mm |
| Width | 60mm – 2500mm |
| Length | 1000mm – 12000mm or as required |
| Standards | ASTM / EN / JIS / GB / DIN |
| Surface Finish | Mill finish, pickled, sandblasted, or coated |
| Heat Treatment | As-rolled, Normalized, Quenched & Tempered (Q+T) |
* Support plasma cutting, beveling, drilling, and edge trimming.
Performance Characteristics and Core Application Areas of Carbon Steel Plates
1. Performance Characteristics
1.1 Mechanical Properties
Strength and Hardness: Carbon content directly affects performance. Low-carbon steel (≤0.25%) has good plasticity and high toughness, suitable for cold working; medium-carbon steel (0.25%-0.60%) has moderate strength, and its overall performance can be improved through heat treatment; high-carbon steel (>0.60%) has high hardness and strong wear resistance, but lower plasticity and toughness.
Processing Performance: Low-carbon steel is easy to weld and stamp, while high-carbon steel requires special treatment (such as quenching and tempering) to reduce brittleness.
1.2 Environmental Adaptability
Corrosion Resistance: Carbon steel is easily oxidized and requires enhanced protection through galvanizing, painting, or alloying (such as weathering steel), especially in humid environments.
Temperature Resistance: The upper limit of long-term operating temperature for ordinary carbon steel is approximately 350°C. For high-temperature environments, heat-resistant steel must be used.
1.3 Economic Efficiency
Low cost, approximately one-third the price of stainless steel, suitable for large-scale production, making it the “king of cost-effectiveness” in industrial materials.
2. Main Applications
2.1 Building Engineering
Structural Support: Low-carbon steel (e.g., Q235B) is used for factory frames and bridge main beams, balancing strength and cost; high-strength steel (e.g., HC340LA) is used for weight reduction in high-rise buildings.
Enclosure Systems: Galvanized carbon steel sheets (e.g., DX51D) are used for roofing and wall panels, improving rust resistance.
2.2 Machinery Manufacturing
Transmission Components: Medium-carbon steel (e.g., 45#) is heat-treated to manufacture gears and shafts, balancing strength and toughness.
Equipment Housings: Cold-rolled steel sheets (e.g., SPCC) are used for machine tool protective covers, with a surface coating to prevent oil stains.
2.3 Automotive Industry
Body Structure: Low-carbon steel sheets (such as DC04) are used for doors and hoods to achieve lightweighting and impact energy absorption; high-strength steel is used for chassis components to increase strength and reduce weight.
2.4 Shipbuilding and Energy
Ship Construction: Marine carbon steel (such as AH36) passes low-temperature impact testing to ensure safety during polar navigation.
Energy Pipelines: Pipeline steel (such as API5L Gr.B) is used for oil and gas transportation, with a yield strength ≥245 MPa.
3. Future Trends
With the development of green buildings, carbon steel sheets are increasingly used in energy-saving projects, such as negative carbon demonstration buildings that use high-performance envelope systems combined with photovoltaic technology to improve energy efficiency.
The above content summarizes the core characteristics and diverse applications of carbon steel sheets, providing a reference for material selection and design.
Processing & Packaging

CNC cutting (plasma / flame) to shape

Blasting and painting (if needed)

Beveling and chamfering

PE wrap + steel pallet or crate
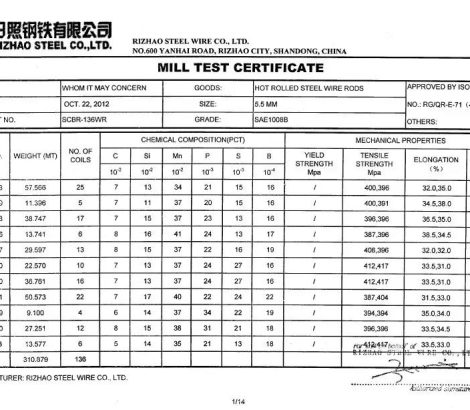
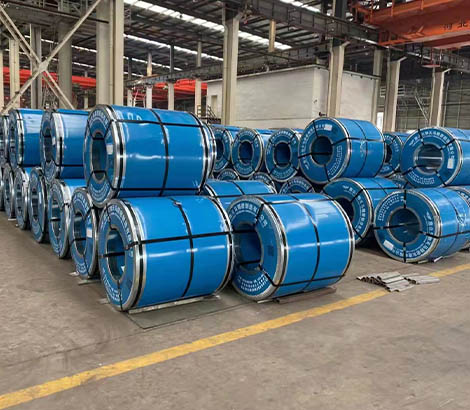
Mill Test Certificate (MTC) included

Why Choose Xishang?
- Large inventory of standard and specialty carbon plates
- Full range of thickness, width, and hardness
- Custom CNC cutting and drilling available
- Fast lead time with export packaging
- One-stop sourcing for structural and pressure grades
- Compliance with ISO/SGS/BV standards


Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between mild steel and structural plate?
Mild steel is low carbon and easily formable; structural plates like Q345 or S355 have higher strength and are used in load-bearing applications.
Q2: Do you supply boiler-grade carbon steel plate?
Yes. We offer ASTM A516, Q245R, and related grades suitable for pressure vessels and tanks.
Q3: Can you cut the plate into parts or flanges?
Absolutely. We support precision plasma cutting to custom drawings.
Q4: What are your available thicknesses?
We stock from 2mm thin sheets to 300mm heavy plates.
Q5: Is carbon steel plate suitable for outdoor environments?
Yes, especially grades like A588 or painted surfaces for weather resistance.

