
- You are here:
- Home /
- Products /
- Alloy /
- High-Strength Steels
High-Strength Steels – Lighter, Stronger, Tougher
We supply structural and alloy steels with high tensile strength, impact resistance and weldability. Ideal for demanding industries such as construction, transportation, mining and machinery.
What Is High-Strength Steel?
High-strength steel (HSS) refers to steels engineered to provide superior yield strength, tensile strength, and impact resistance while allowing for weight reduction and structural efficiency.
It includes:
Structural high-strength steel: Q460, Q690, S690QL, S960QL
Alloy tool steels: 42CrMo4, 4130,4140,4340,5140, 8620, 34CrNiMo6,Nitr0nic60/S21800,XM-19,SUH616,961
Tempered & quenched steels: for wear and dynamic loading
Advantages:
High strength-to-weight ratio
Excellent formability and weldability
Fatigue resistance under cyclic load
Toughness at low and high temperatures
Products Link
- Alloy >>
- Heat-Resistant Steel
- Inconel Alloys
- Urea-Grade Steel
- Titanium Alloys
- Superalloys
- Super Duplex Stainless Steels
- Special Stainless Steels
- Soft Magnetic Alloys
- Precipitation Hardening Stainless
- Hydropower Steel
- Incoloy Alloys
- Super Austenitic Stainless Steels
- High-Strength Steels
- Monel Alloys
- Hastelloy Alloy
- Cobalt Based Alloy
- Stainless Steel >>
- Galvanized Steel >>
- Carbon Steel >>
- Aluminum Steel >>
Optional product specifications
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Forms | Plate, sheet, bar, rod, pipe, forging blank |
| Thickness (Plate) | 4mm – 150mm |
| Bar Diameter | 10mm – 600mm (round / square) |
| Grades | Q460D, Q690D, Q890E, S690QL, 42CrMo4, 8620, 4130, 4140,4340, 5140, 30CrMnSiA |
| Standards | GB/T 16270, EN 10025-6, DIN 42CrMo4, ASTM A514 |
| Condition | Hot rolled, forged, quenched & tempered (Q+T) |
| Mechanical Tests | Yield, tensile, impact (Charpy V), hardness |
Certificates available: EN10204 3.1 / 3.2, CE, DNV, SGS, TUV.
High-strength steel plays a vital role in modern industry, its superior performance and wide range of applications making it a key material. The following is a detailed analysis of its performance characteristics and uses:
1. Performance Characteristics
1.1 High Strength
High Tensile Strength: High-strength steel has significantly higher tensile strength than ordinary steel, capable of withstanding greater external forces without easily deforming or breaking, making it suitable for structures requiring high load-bearing capacity.
Excellent Yield Strength: Under stress, high-strength steel remains stable, preventing premature plastic deformation and ensuring structural integrity.
1.2 Lightweight Advantages
Lightweight: At the same strength, high-strength steel is lighter than ordinary steel, helping to reduce the overall structural weight, improve energy efficiency, and enhance portability.
Material Savings: The lightweight characteristic reduces material usage, lowering costs and resource consumption.
1.3 Durability and Fatigue Resistance
Strong Corrosion Resistance: Through special processes, such as galvanizing or coating, it effectively resists environmental corrosion, extending its service life.
Excellent fatigue resistance: Under cyclic loading, high-strength steel maintains long-term stability, reducing the risk of crack propagation.
2. Applications
2.1 Automotive Industry
Body Structure: Used to manufacture lightweight body structures, improving fuel efficiency and safety.
Chassis Components: Such as suspension systems and drive shafts, which need to withstand high dynamic loads, high-strength steel provides reliable support.
2.2 Construction Industry
High-Rise Buildings: Used for steel structural frames, enhancing earthquake and wind resistance.
Bridge Engineering: In large bridges, high-strength steel ensures long-term stability and load-bearing capacity.
2.3 Machinery Manufacturing
Heavy Equipment: Such as excavators and cranes, which need to withstand extreme working conditions, high-strength steel provides the necessary strength and durability.
Precision Components: Used to manufacture high-precision mechanical parts, ensuring equipment operating efficiency and reliability.
2.4 Energy Sector
Wind Power Equipment: In wind turbine towers and blades, high-strength steel supports the structure and resists environmental stresses.
Oil pipelines: Used to transport high-pressure oil and gas, ensuring the safe operation of pipeline systems.
3. Summary
High-strength steel products, with their advantages of high strength, lightweight, and durability, are widely used in the automotive, construction, machinery, and energy sectors, providing reliable solutions for modern industry.
Processing & Packaging

Flame / laser / plasma cutting

Precision milling, turning, drilling,embossed

Hardness, impact, tensile testing before dispatch

Protective rust-proof coating + film wrapping
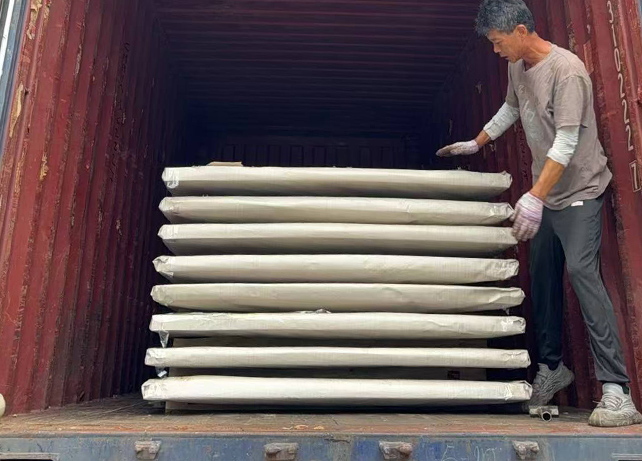

Bundled with steel straps or packed in wooden crates
Why Buy From Xishang?
- Wide inventory from structural grades to alloy steels
- Cutting, pre-machining, quenching & tempering in-house
- Expert support for equivalent grade selection
- Guaranteed mechanical properties and UT/NDT tested
- Stable supply for both OEM and project orders
- Logistics support for bulk, containerized and LCL shipping


Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What’s the difference between Q690D and S690QL?
A:
Q690D is a Chinese standard high-strength low-alloy steel, while S690QL is a European EN10025-6 quenched and tempered grade. Both offer ~690MPa yield strength.
Q2: Do you supply tempered bars like 42CrMo4 Q+T?
A:
Yes. We stock and process quenched and tempered bars up to 600mm diameter.
Q3: Can high strength steel be welded?
A:
Yes, but proper preheat, filler selection and post-weld treatment are required. We provide WPS and guidance.
Q4: Do you provide MTC and impact testing?
A:
Absolutely. MTC with yield/tensile/impact values are provided with every batch.
Q5: Do you accept custom-cut or small lot orders?
A:
Yes. Cut-to-size and MOQ flexibility available especially for project sourcing.
Q6: 4130vs4140vs4340
4130 vs 4140 vs 4340
| Property/ Grade | 4130 (30CrMo) | 4140 (42CrMo) | 4340 (40CrNiMoA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Content | 0.28-0.33% | 0.38-0.43% | 0.38-0.43% |
| Chromium Content | 0.80-1.10% | 0.80-1.10% | 0.70-0.90% |
| Molybdenum Content | 0.15-0.25% | 0.15-0.25% | 0.20-0.30% |
| Nickel Content | ≤0.35% | ≤0.35% | 1.65-2.00% |
| Tensile Strength | ≥930 MPa | ≥1000 MPa | ≥1080 MPa |
| Yield Strength | ≥785 MPa | ≥930 MPa | ≥930 MPa |
| Elongation | ≥12% | ≥9% | ≥12% |
| Impact Energy | ≥63 J | ≥47 J | ≥63 J |
| Weldability | Good, requires preheating above 175°C | Poor, needs strict process control | Poor, needs strict process control |
| Heat Treatment | Quenching + Tempering, Tempering at 540-650°C | Quenching + Tempering, Higher Tempering Temperature | Quenching + Tempering, Higher Tempering Temperature |
| Typical Applications | Aircraft landing gear, engine mounts, drill collars, high-pressure pipelines, automotive transmission components | Heavy-duty molds, high-strength gears, shaft components | Ultra-high-strength parts, aircraft landing gear, critical components in heavy machinery |
Material Selection Recommendations
- Prioritize 4130 when high toughness and good weldability are needed, such as in aerospace, oil equipment, and automotive transmission parts.
- Choose 4140 for applications requiring high strength and wear resistance, like heavy machinery molds, gears, and shaft components.
- Opt for 4340 when ultra-high strength and toughness are essential, such as in critical parts under extreme stress.



